Nov 8, 2023answered • expert verified 2. Which statement best compares a carbohydrate and a nucleic acid? A. The sequence of monomers in a carbohydrate stores genetic information, and the bonds in a nucleic acid store energy. B. The bonds in a carbohydrate store energy, and the sequence of nucleotides in a nucleic acid stores genetic information. I C.
OCR Biology A- 3.9 DNA Replication and the Genetic Code | Teaching Resources
Which statement correctly compares nucleic acids and carbohydrates? They both contain carbon, but only nucleic acids contain hydrogen. They both contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio.

Source Image: scribd.com
Download Image
Answer: The correct answer is they both contain carbon but only nucleic acid contain phosphorous. Explanation: Carbohydrates are Polyhydroxy aldehydes or Polyhydroxyketones .Carbohydrates are composed of carbon,hydrogen and oxygen .The general formula of carbohydrate is CnH2nOn.

Source Image: pinterest.com
Download Image
Full article: Fluorophore tagged bio-molecules and their applications: A brief review
How do nucleic acids compare to carbohydrates? Flexi Says: Nucleic acids are the macromolecules that make up the genetic material of organisms. Their main function is to store and process the genetic information. Unlike the carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins, nucleic acids are not involved in metabolic process for energy production in body.

Source Image: teachingexpertise.com
Download Image
Which Statement Correctly Compares Nucleic Acids And Carbohydrates
How do nucleic acids compare to carbohydrates? Flexi Says: Nucleic acids are the macromolecules that make up the genetic material of organisms. Their main function is to store and process the genetic information. Unlike the carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins, nucleic acids are not involved in metabolic process for energy production in body.
Which statement correctly compares nucleic acids and carbohydrates? A) They both contain carbon, but only nucleic acids contain hydrogen. B) They both contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio. C) They both contain carbon, but only carbohydrates contain oxygen. D) They both contain carbon, but only nucleic acids contain phosphorous.
Building Blocks of Life: 28 Macromolecules Activities – Teaching Expertise
The correct statement that compares nucleic acids and carbohydrates is option C) They both contain carbon, but only carbohydrates contain oxygen. Nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA, are composed of nucleotide building blocks.
SOLVED: Please help me Compare and contrast the difference between the 4 macromolecules of life: Proteins, Carbohydrates, Lipids and Nucleic Acids. Be sure to include the elements that make up each, their
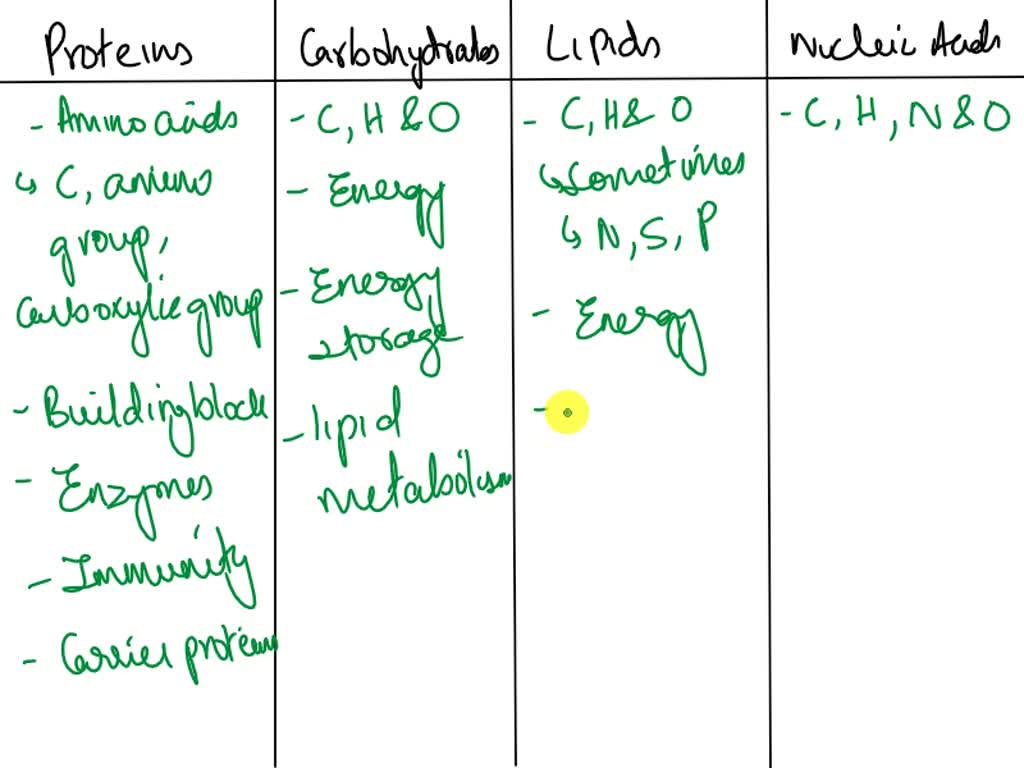
Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
Biomolecules Stock Illustrations – 307 Biomolecules Stock Illustrations, Vectors & Clipart – Dreamstime
The correct statement that compares nucleic acids and carbohydrates is option C) They both contain carbon, but only carbohydrates contain oxygen. Nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA, are composed of nucleotide building blocks.
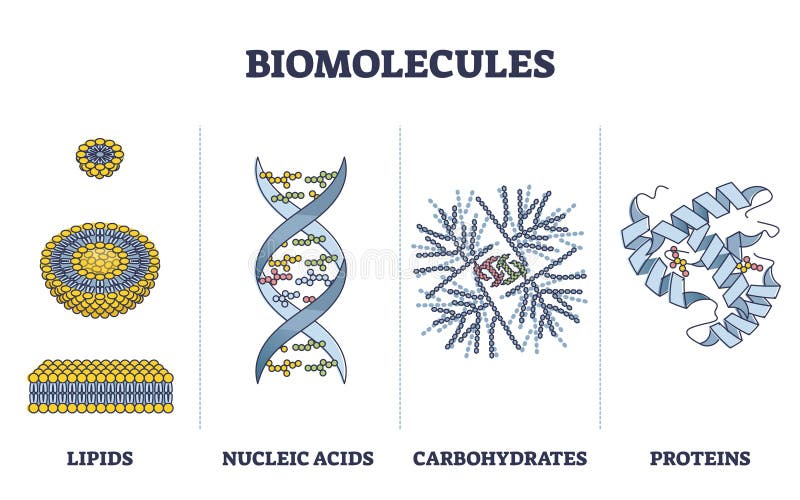
Source Image: dreamstime.com
Download Image
OCR Biology A- 3.9 DNA Replication and the Genetic Code | Teaching Resources
Nov 8, 2023answered • expert verified 2. Which statement best compares a carbohydrate and a nucleic acid? A. The sequence of monomers in a carbohydrate stores genetic information, and the bonds in a nucleic acid store energy. B. The bonds in a carbohydrate store energy, and the sequence of nucleotides in a nucleic acid stores genetic information. I C.

Source Image: tes.com
Download Image
Full article: Fluorophore tagged bio-molecules and their applications: A brief review
Answer: The correct answer is they both contain carbon but only nucleic acid contain phosphorous. Explanation: Carbohydrates are Polyhydroxy aldehydes or Polyhydroxyketones .Carbohydrates are composed of carbon,hydrogen and oxygen .The general formula of carbohydrate is CnH2nOn.

Source Image: tandfonline.com
Download Image
Macronutrients: Carbohydrates, Lipids, Protein – Nutrition – LevelUpRN
In Summary: Comparing Biological Macromolecules. Proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids are the four major classes of biological macromolecules—large molecules necessary for life that are built from smaller organic molecules. Macromolecules are made up of single units known as monomers that are joined by covalent bonds to form

Source Image: leveluprn.com
Download Image
A framework to extract biomedical knowledge from gluten-related tweets: The case of dietary concerns in digital era – ScienceDirect
How do nucleic acids compare to carbohydrates? Flexi Says: Nucleic acids are the macromolecules that make up the genetic material of organisms. Their main function is to store and process the genetic information. Unlike the carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins, nucleic acids are not involved in metabolic process for energy production in body.

Source Image: sciencedirect.com
Download Image
Food: emotion, imagination and reality – British Association for Holistic Medicine & Health Care
Which statement correctly compares nucleic acids and carbohydrates? A) They both contain carbon, but only nucleic acids contain hydrogen. B) They both contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio. C) They both contain carbon, but only carbohydrates contain oxygen. D) They both contain carbon, but only nucleic acids contain phosphorous.

Source Image: bhma.org
Download Image
Biomolecules Stock Illustrations – 307 Biomolecules Stock Illustrations, Vectors & Clipart – Dreamstime
Food: emotion, imagination and reality – British Association for Holistic Medicine & Health Care
Which statement correctly compares nucleic acids and carbohydrates? They both contain carbon, but only nucleic acids contain hydrogen. They both contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio.
Full article: Fluorophore tagged bio-molecules and their applications: A brief review A framework to extract biomedical knowledge from gluten-related tweets: The case of dietary concerns in digital era – ScienceDirect
In Summary: Comparing Biological Macromolecules. Proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids are the four major classes of biological macromolecules—large molecules necessary for life that are built from smaller organic molecules. Macromolecules are made up of single units known as monomers that are joined by covalent bonds to form